CCEA GCSE Geography > River Environments > The Drainage Basin: A component of the water cycle
The drainage basin: a component of the water cycle
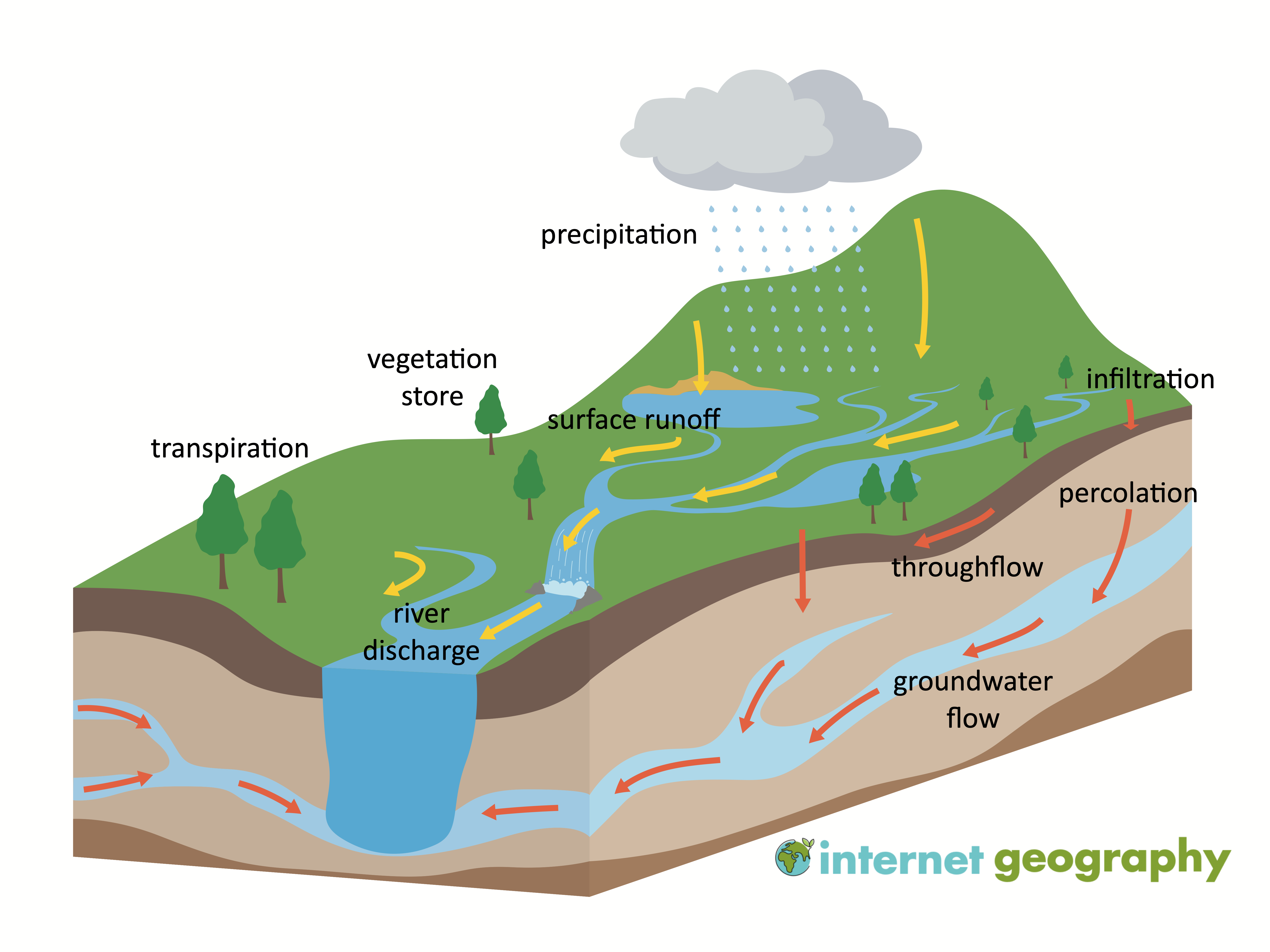
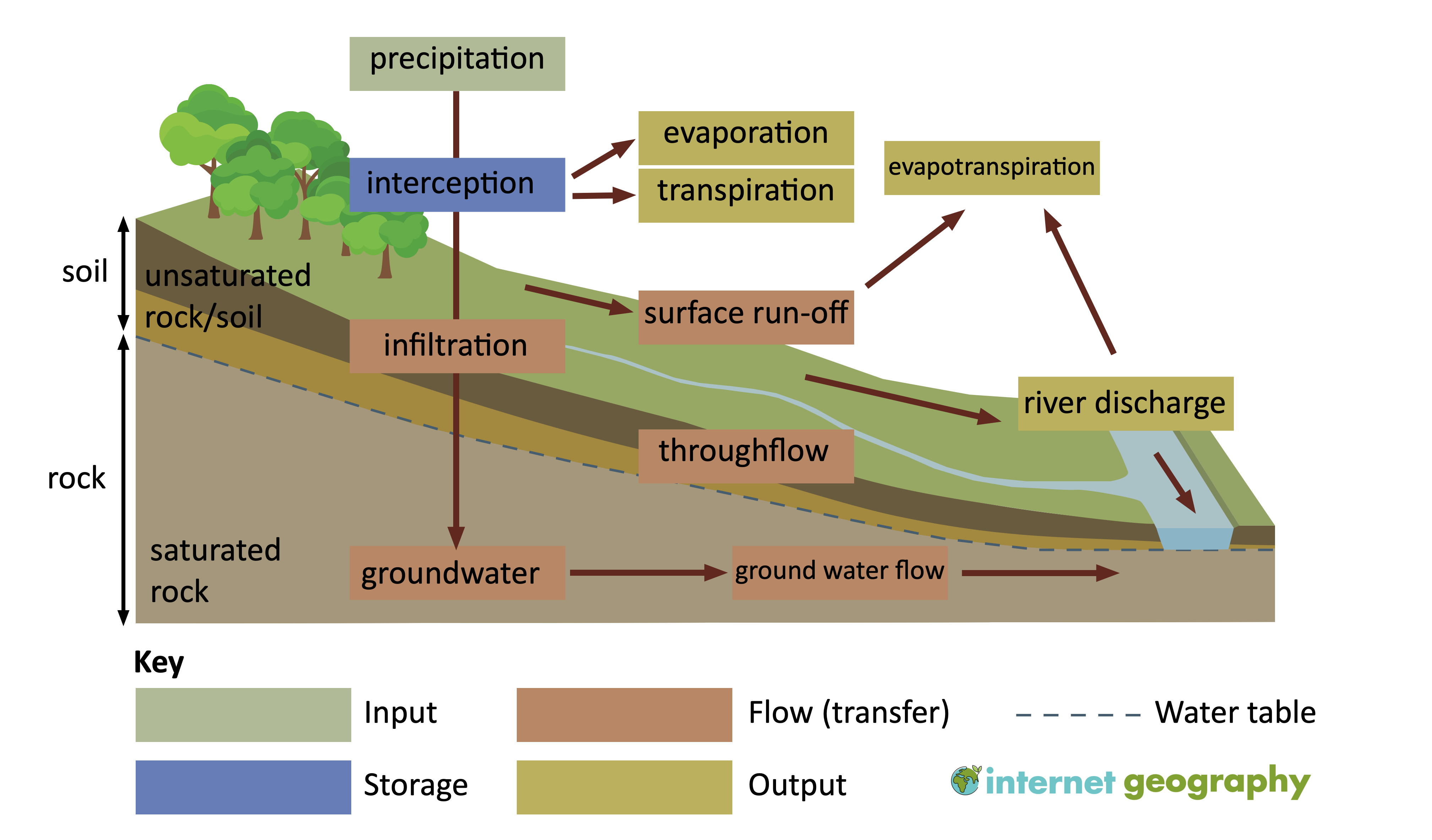
A drainage basin is an area of land where water from precipitation collects and flows into a common outlet, such as a river or a lake. Drainage basins are essential components of the Earth’s water cycle and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of water resources. In this section, we will explore the various elements of the drainage basin system and their interrelationships.
Inputs
Precipitation is the primary input of water into a drainage basin. It includes various forms of moisture, such as rain, snow, hail, and sleet. The amount and type of precipitation vary depending on geographic location, climate, and season. Precipitation provides water for various processes within the drainage basin system.
Stores
Vegetation within a drainage basin serves as a store for precipitation. When rain falls, some of it is intercepted by leaves, branches, and other plant surfaces, preventing it from reaching the ground directly. This intercepted water is either evaporated back into the atmosphere, absorbed by the plants or later transpired.
Transfers
Transfers refer to water movement within the drainage basin from one location to another. There are several processes involved in water transfers:
Outputs
Outputs refer to how water leaves the drainage basin system. The two main outputs are: