Rivers Flashcards
Click to View the Question
Friction with the river bed and banks can reduce the velocity of the river leading to deposition.
Find out more about river deposition.
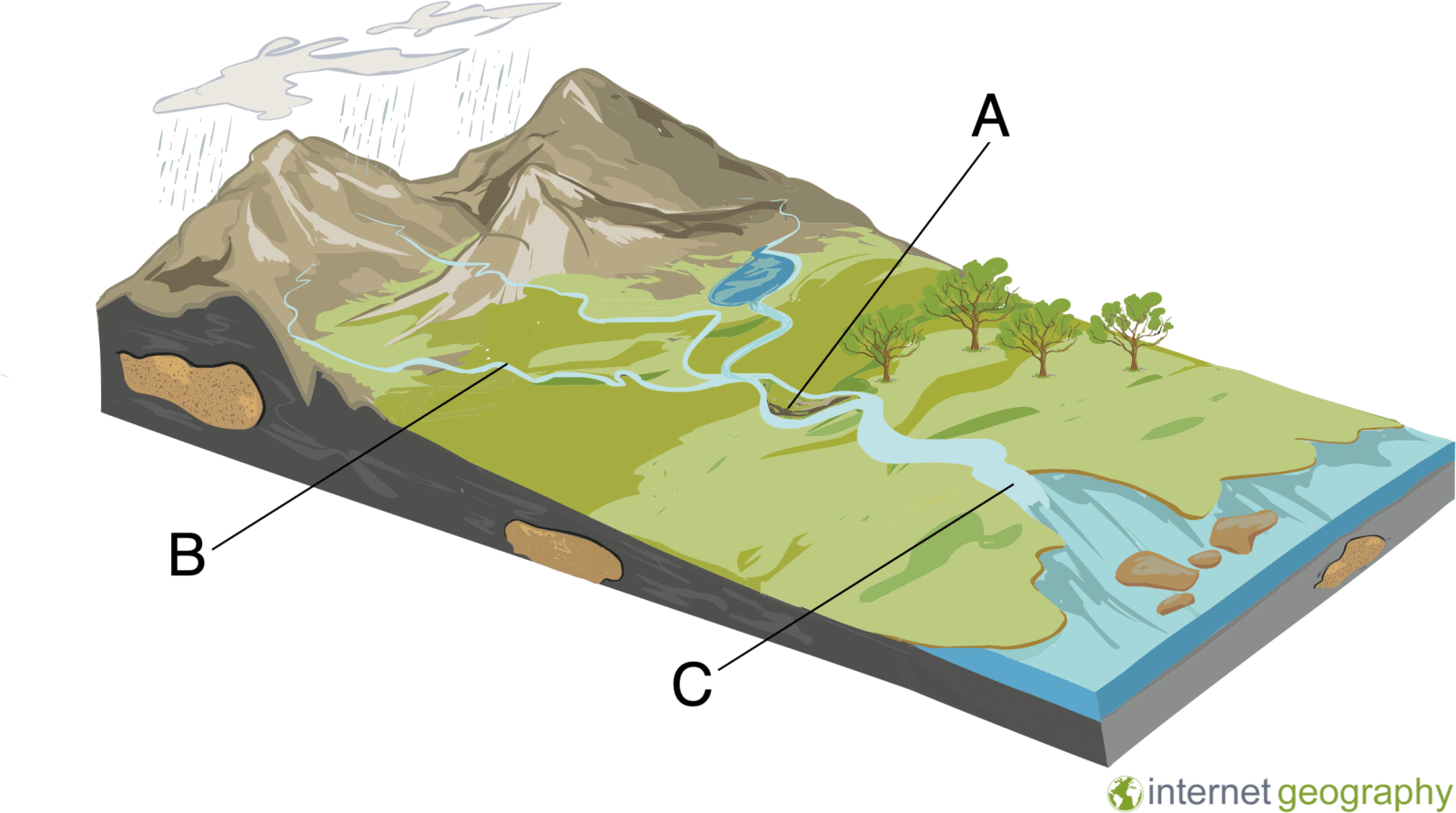
Why might deposition occur at site B on the diagram below?
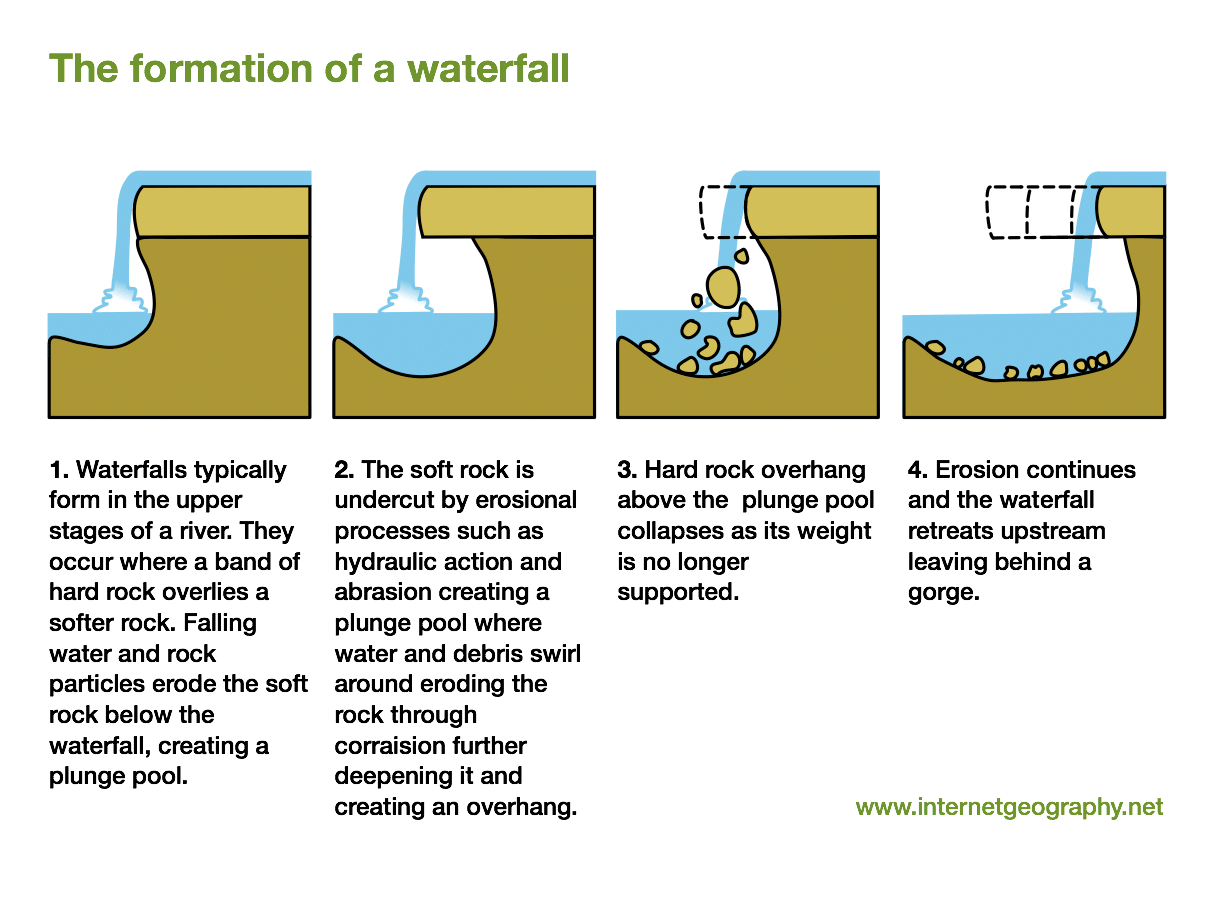
Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of a waterfall.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Find out more about the landforms of erosion in the upper course of a river.
Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of a waterfall.
Click to View the Question
Suspension
Find out more about river transportation.
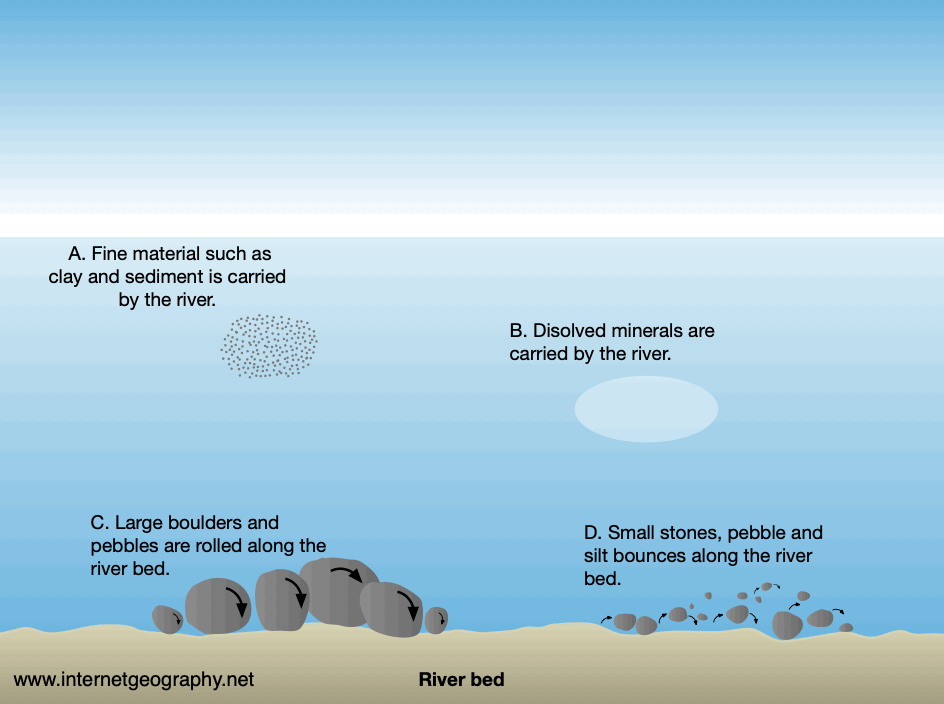
Identify the type of transportation labelled A on the diagram below.
How does a channel cross-section change downstream?
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
In the upper course, the channel is very narrow and very shallow. By the middle course, the channel becomes wider and deeper usually over 1 m. By the lower course, the channel becomes wider still and the channel is much deeper.
Find out more about the cross profile of a river.
How does a channel cross-section change downstream?
Give two benefits of planting trees as a flood management strategy.
Click to View the Answer
Click to View the Question
Examples include:
- benefits wildlife by creating habitats
- it’s a natural method of intercepting precipitation and slowing water transfer in a river basin
- absorbs and stores carbon reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
- relatively inexpensive.
Find out more about soft engineering.
Give two benefits of planting trees as a flood management strategy.