Natural Population Change
Natural population change is the difference between the number of live births and deaths during a given time period (usually one year). It can be either positive or negative. If birth rates (number of live births per 1000 people) are higher than death rates, then a population will increase. If the death rate (number of deaths per 1000 per year) for an area is higher than birth rates, the population will decrease.
Births and deaths are natural causes of population change. The difference between birth and death rates is called the natural increase/decrease.
The Demographic Transition Model attempts to show how the population of country or region changes as it develops.
The model is divided into five stages.
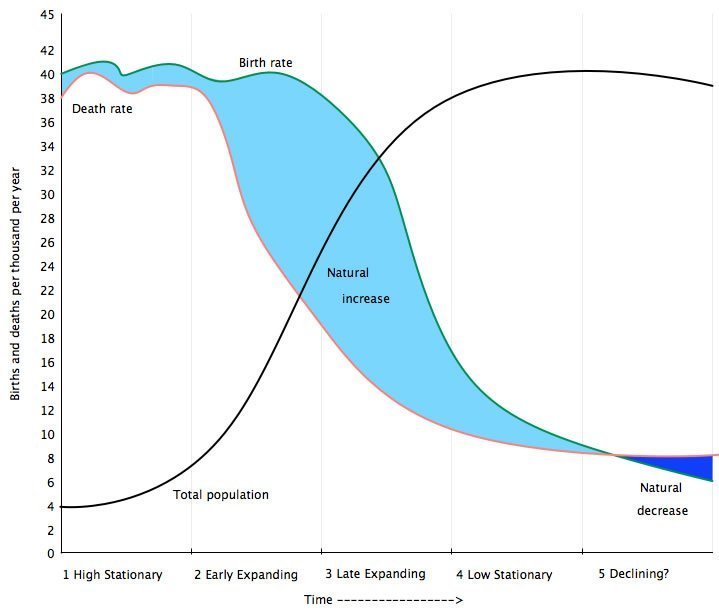
The demographic transition model
Stage 1
Birth rate and death rate are high – low natural increase – low total population
Stage 2
The birth rate is high – the death rate is falling – high natural increase (population growth)
Stage 3
Falling birth rate – low death rate – high natural increase (population growth)
Stage 4
Birth rate and the death rate is low – low natural increase – high total population
Stage 5
The birth rate is lower than the death rate – natural decrease in population
The Demographic Transition Model does not take into account migration, another factor that can cause the population to both increase and decrease.
Social impacts of a high rate of natural increase
- More schools will be needed
- Health services will need to accommodate the needs of young people including more midwives and health care professionals to work in clinics to vaccinate, immunise and support young infants.
Economic impacts of a high rate of natural increase
- The demand for food will increase, leading to either greater agricultural production or the need to import more food
- The economy will need to expand to provide more job opportunities otherwise there will be high levels of unemployment
- There will be a greater pool of labour which can stimulate economic production and growth
- Taxation may increase to fund the expansion of social and health care as well as education
The impact of HIV/AIDS
There are several countries in the world where death rates are rising. One major cause of this is HIV/AIDS. This particularly affects the continent of Africa. In the 12 countries worst affected in Africa, 1 in 10 people between 15 and 49 are HIV positive. There are a number of impacts of this:
- As more people of working age become infected there will be fewer people available to work which can affect economic development in the country.
- There are thousands of orphaned children in Africa, where there are no grandparents to look after children following the loss of their parents.
- The lack of money spent on educating people about how to avoid HIV/AIDS means some people are not aware of the steps they can take to protect themselves.
- People are unable to afford the costs of drugs to treat the disease.
- The number of infant and child deaths is increasing as mothers pass on HIV when they are pregnant.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.



