World Population Increase
Despite birth rates falling, world population continues to grow as people are living longer. In 2018 the population of Earth was estimated to be 7,631,091,000 by the United Nations. In the video below, Professor Hans Rosling provides an overview of world population growth and predictions for the future.
How Did the World Population Change? from Gapminder on Vimeo.
Predictions by the UN suggest world population will continue to grow, though more slowly, in the future. The graph below shows world population to 2018, followed by a range of estimates of how it will continue to grow.
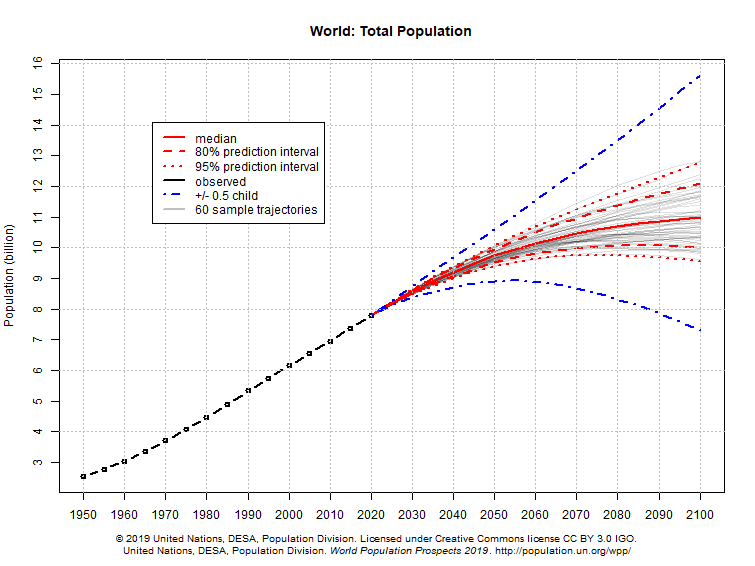
World population projections
So, how reliable are these estimates? The answer is very.
In this short video, Professor Hans Rosling shows that already back in the 1950’s the UN population experts were able to predict very precisely the population growth for the next 50 years. The forecasts made today predict that by the end of the century, there will be around 11 billion people in the world. The track record of the UN statisticians shows that their global forecasts have been very accurate historically.
How Reliable is the World Population Forecast? from Gapminder on Vimeo.
The graph below shows the growth rate of the world’s population is slowing down. Today, the annual world population growth rate is almost half it was during its peak in the 1960s.
Population growth rates significantly vary between the continents. Asia has the highest population with 6.4 billion people. The worlds two most populous countries, China and India, account for 37% of the world’s population.
Despite Asia having the largest population, its rate of natural population increase is declining. Whereas, the natural population increase in Africa remains high. This region will, in the future, see a significant increase in population which will bring a range of challenges to the continent including the provision of a reliable water and food supply.
Reasons for rapid population growth – 1750-1900
Birth rates and death rates were high up to 1750 meaning there was little growth in world population. From 1750 death rates dropped rapidly to about 20 deaths per 1000 people and birth rates (35 live births per 1000) remained high.
Death rates fell due to:
- improvements in agriculture meaning food supplies increased, reducing malnutrition and starvation.
- public healthcare and medical breakthroughs, including the introduction of vaccinations, led to fewer deaths
- scientific knowledge grew and people became more aware of the importance of hygiene
- water supplies and sewerage provision improved, reducing deaths caused by diarrhoea
These factors led to an increase in life expectancy. As the birth rate remained high, world population began to grow.
Reasons for rapid population growth – 20th Century
World population growth accelerated rapidly during the 20th Century. Although birth rates fell to around 20 live births per 1000 death rates also continued to fall, to around 15 per 1000 people. Life expectancy continued to increase leading to a population explosion.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.



