Employment Structures
Employment structure means how the workforce is divided up between the three main employment sectors – primary, secondary and tertiary. Employment structures change over time.
Countries in the early stage of development usually have a high percentage of the population in primary employment. This is because most people are engaged in agricultural activities.
As a country begins to develop an industrial base there is an increase in the secondary sector. An increase in machinery on farms means fewer people are needed. People tend to migrate to urban areas to get jobs in factories.
When a country becomes more economically developed there is a greater demand for services such as education, healthcare and tourism. Therefore the tertiary sector undergoes growth. By this time computers, machinery and robots replace people in the secondary sector hence the decrease in secondary jobs.
Employment structures are usually displayed as pie charts:
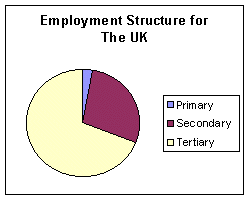
Uk employment structure pie chart
The UK is a HIC or high-income country. It has a low proportion of people working in the primary industry. This is partly because of mechanisation. Machinery has taken over jobs in the primary sector. Also, as primary resources have become exhausted (e.g. coal) The UK now imports a considerable amount of its non-renewable resources. The number of people employed in the secondary sector is falling. This is because fewer people are needed to work in factories as robots are taking over jobs. The tertiary sector is the main growth area. Most people work in hospitals, schools, offices and financial services. Also, as people have more free time and become wealthier there is a greater demand for leisure services. Therefore more jobs become available in the tertiary sector.
Brazil is a MIC (medium income country). While it is developing its economic base there are still a large number of people employed in primary industries such as farming. There is a large proportion of people employed in tertiary industries. One reason for this is because of the growth of Brazil as a tourist destination. Also, there have been significant improvements in the provision of health care, education and transport.
Ghana is an LIC or low-income country. The majority of people work in the primary sector. This is due to the lack of machinery available in farming, forestry and mining. Farming is very important because people often grow the food they eat. Few people work in secondary industries due to the lack of factories – machinery is too expensive and multi-national companies rely on the raw materials available in Ghana to assist in manufacturing products.
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.