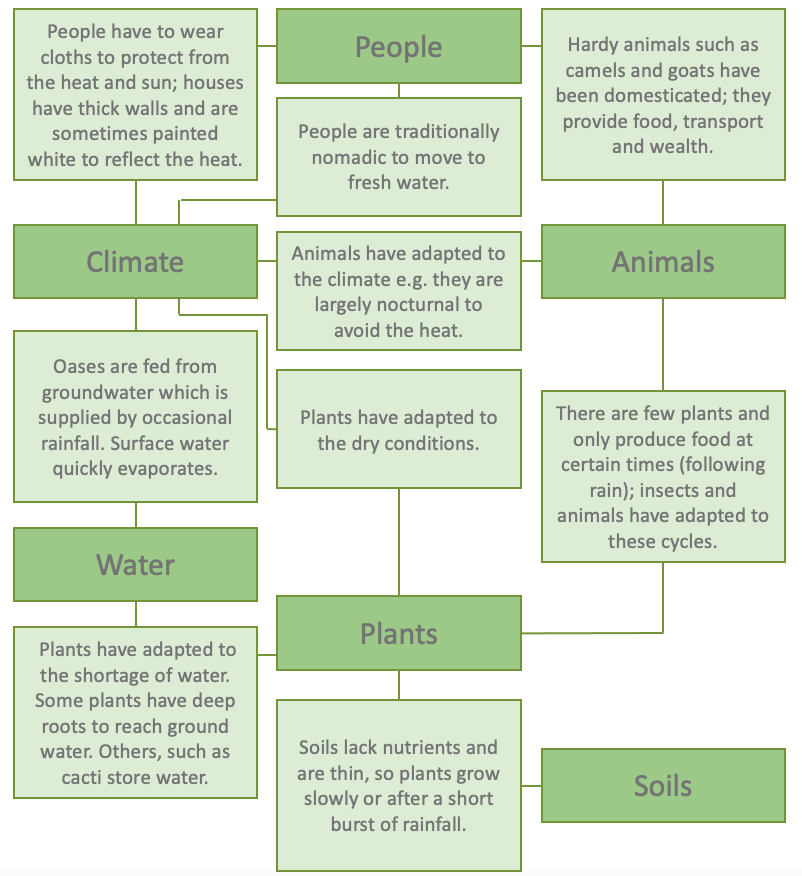
Interdependence in the hot desert
As in all ecosystems, the different parts are lined together and depend on each other, especially in a food web with many more plants than animals.
Interdependence between the different components (climate, water, soils, plants, animals and people) of the hot desert is essential for life to thrive. The living components of the hot desert and the physical environment are connected. For example, people depend on their animals for milk and food and their use as pack animals. Humans are also dependent on water for their survival.
Other examples of interdependence include:
- complex food webs involving energy and nutrients gained from water, soils and vegetation being transferred between different species.
- the sustainable co-existence of humans, plants and animals in semi-arid environments.
- the damage that human actions, such as overgrazing and over-cultivation, can cause to the natural environment.
- indigenous people, such as nomadic tribes, have adapted to climatic conditions and natural patterns. Crops are difficult to grow, so nomadic tribes keep animals such as goats and camels and move them from one water source to the next, also avoiding overgrazing as climatic conditions mean vegetation often cannot recover.
- the impact of climate change on water, soils, plants, animals and people.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.