The impacts of rainforest deforestation in Malaysia
What are the impacts of rainforest deforestation in Malaysia?
The graph below shows the impact of deforestation on natural forest cover in Malaysia.
The map below shows the location of deforestation in Malaysia. The areas shaded green are primary forests, whereas the pink areas show deforestation.
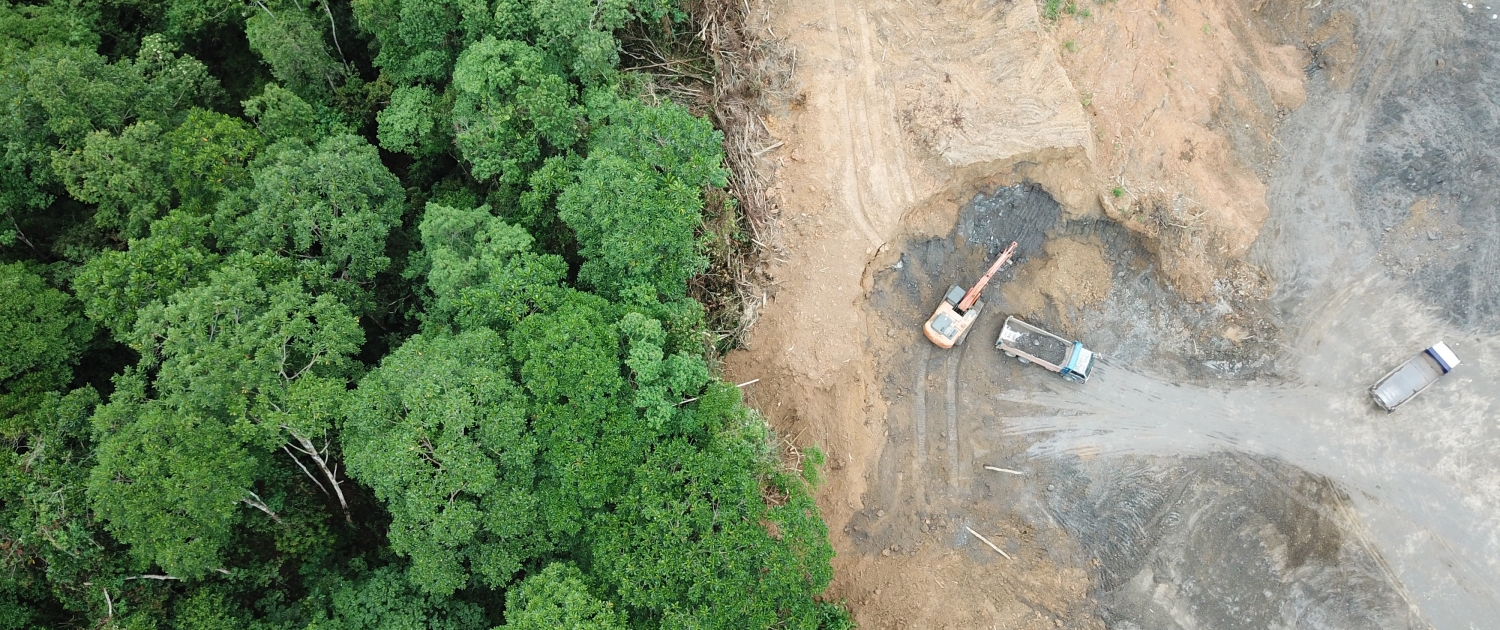
Deforestation
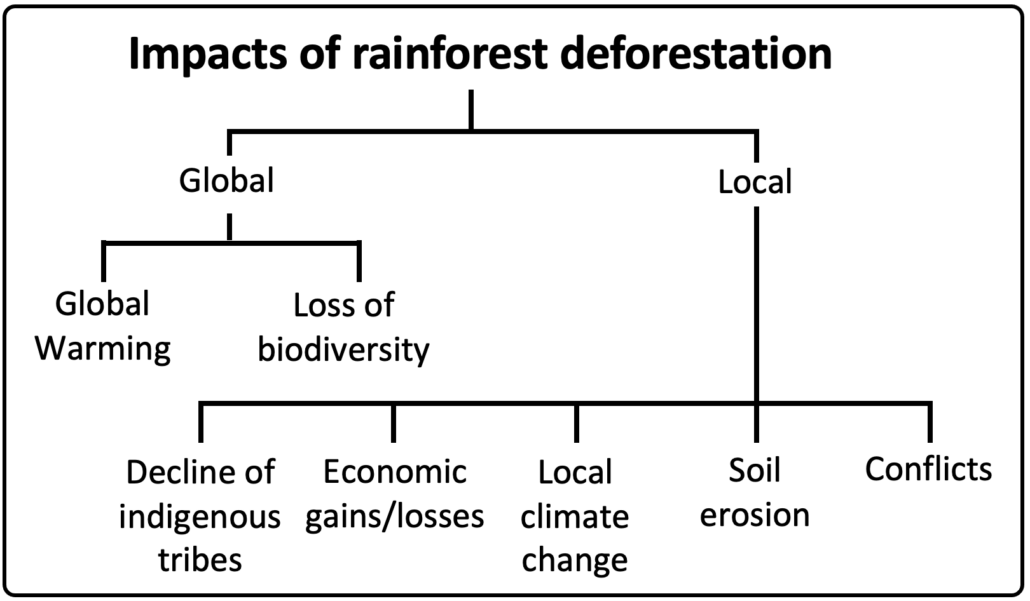
in Malaysia has had a range of local and global impacts.
What are the global impacts of rainforest deforestation in Malaysia?
Global Warming
The Malaysian rainforest is significant at a global level. The tree canopy absorbs carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. As soon as trees are felled, this stops, and more carbon dioxide remains in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is also released when fire is used to clear the rainforest. In these ways, deforestation is a major contributor to climate change.
Loss of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of plant and animal life in the world or a particular habitat. Rainforests are the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet. Clearing the rainforest means reduced biodiversity, and individual species can become endangered or extinct.
Species richness surveys in Malaysia show a 34.9% reduction in species richness in oil palm compared to forest habitats, and 79.6% of the species found in forest habitats were not found in oil palm habitats.
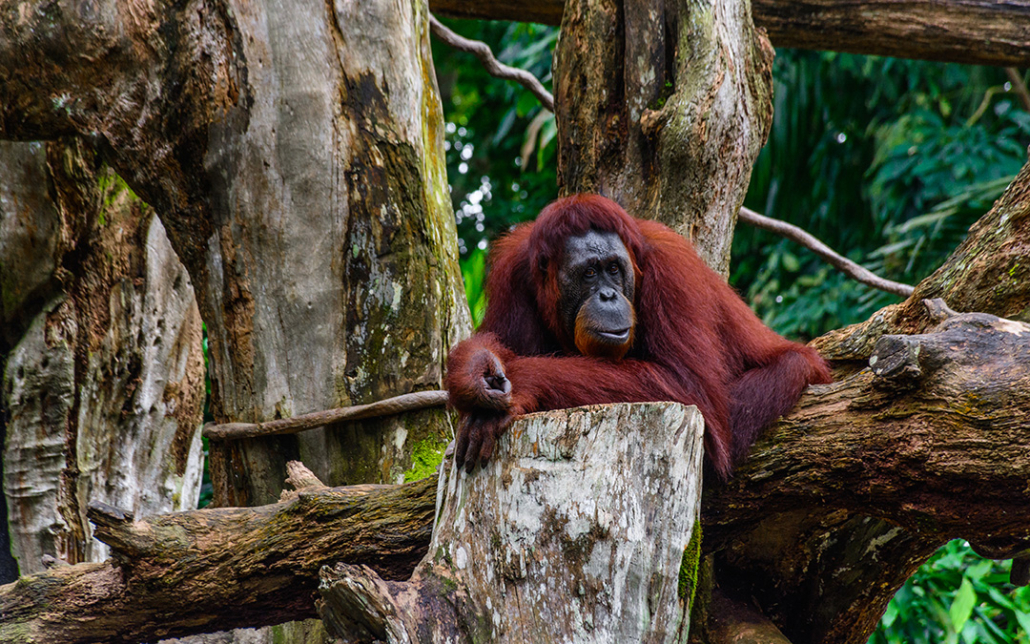
Species at risk in the Malaysian rainforest include Pygmy Elephants, Orangutans, Sumatran Rhinos and Malayan Tigers, all endangered.
As species are lost, so are many possible cures for life-threatening diseases.
What are the local impacts of rainforest deforestation in Malaysia?
Local Climate Change
Forests have been termed the “air conditioners” of the landscape because they keep things cool by evaporating water. The evaporated water forms clouds, which also contribute to cooling. If evaporation is not happening, then much of the sun’s energy goes into raising temperatures instead.
The clouds reflect a lot of the sun’s radiation back into space and are a source of rainfall. So when tropical forests are felled, local temperatures tend to rise, and rainfall patterns change, becoming less reliable and more extreme.
Therefore, deforestation reduces evapotranspiration, making the local area drier and increasing local temperatures.
The Decline of Indigenous Tribes
Malaysia’s Orang Asli have been stripped of historic lands and are more susceptible to deadly illness.
Loss of forest due to illegal logging has significantly reduced the bat population. Bats are a natural means by which fruit crops are pollinated, so there is an enormous impact on indigenous people and their food security when the forest is illegally cleared (a) because the food source has directly been removed through illegal logging and (b) because the bat population is no longer available to pollinate the wider forest area. Malaysia now has a situation where some communities have to pollinate fruit trees by hand. The problem is exacerbated by the increased use of pesticides, which further cause problems in maintaining wildlife and rainforest. Pesticides are being used more because the bat population no longer provides the natural means by which insect populations are managed.
Soil Erosion
Soil takes thousands of years to form. However, it can be stripped away very quickly. The removal of soil by rain and wind is known as soil erosion. The roots of vegetation, such as trees, bind the soil together. Once vegetation is removed, it becomes loose and can be easily eroded.
Additionally, when soil is exposed, nutrients are leached away by heavy rain, making the soil infertile.
A significant amount of carbon is stored in rainforest soils. Soil erosion releases the stored carbon into the atmosphere, enhancing the natural greenhouse effect and contributing to climate change.
Conflict
Disputes between the state companies and indigenous people end in conflict.
Pollution
Pollution of water sources through activities such as mining results in water shortages.
Economic Gains/Losses
It is estimated that illegal logging denies revenues to the people of Malaysia in the order of USD 500m per annum. It is also clear that indigenous people are having their land and, therefore, sources of food and livelihood denied to them at a cost exceeding USD 800 million per annum in compensation and welfare payments.
Illegal logging leads to the loss of forest biodiversity and ecosystem services deprives local communities of their rights and livelihoods and generates approximately US$10–15 billion annually in criminal proceeds. In national revenue terms, the World Bank estimates that Governments lose around USD 5 Billion per annum in direct taxation. Illegal logging can refer to timber from restricted forests, harvesting protected species or over allowable yields, harvesting in violation of land or tenure rights, and failing to pay taxes and royalties.
As areas become less biodiverse, the tourism industry may be negatively impacted.
As climate change is exacerbated by deforestation, produce yields may decrease due to the drier, hotter climate, which will influence trade and the economy.
Mining, logging, agriculture, hydroelectric power, and road building provide local people with jobs and increased incomes.
Products from tropical rainforest lands can be traded with other countries for profit. The palm oil industry has been the fourth-largest sector contributing to the economy for 15 to 18 years. In 2020, palm oil accounted for thirty-eight per cent of the value of Malaysia’s agricultural output and three per cent of its gross domestic product. The palm oil industry employs 441,000 people, half of whom are small landowners.
Companies that exploit rainforests pay taxes, supporting economic development and providing public services, such as healthcare and education.
Improved accessibility to rainforests through the construction of roads supports the tourist industry and connects rural to urban areas, further supporting economic development.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.