What are natural hazards?
AQA GCSE Geography > The Challenge of Natural Hazards > What are natural hazards?

What are Natural Hazards?
A natural hazard is a natural event (for example, flood, volcanic eruption, earthquake, tropical storm) that threatens people or has the potential to cause damage, destruction and death.
Types of Natural Hazard
Natural hazards are most commonly classified by the physical processes that caused them.
Tectonic hazards are created through the movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates.
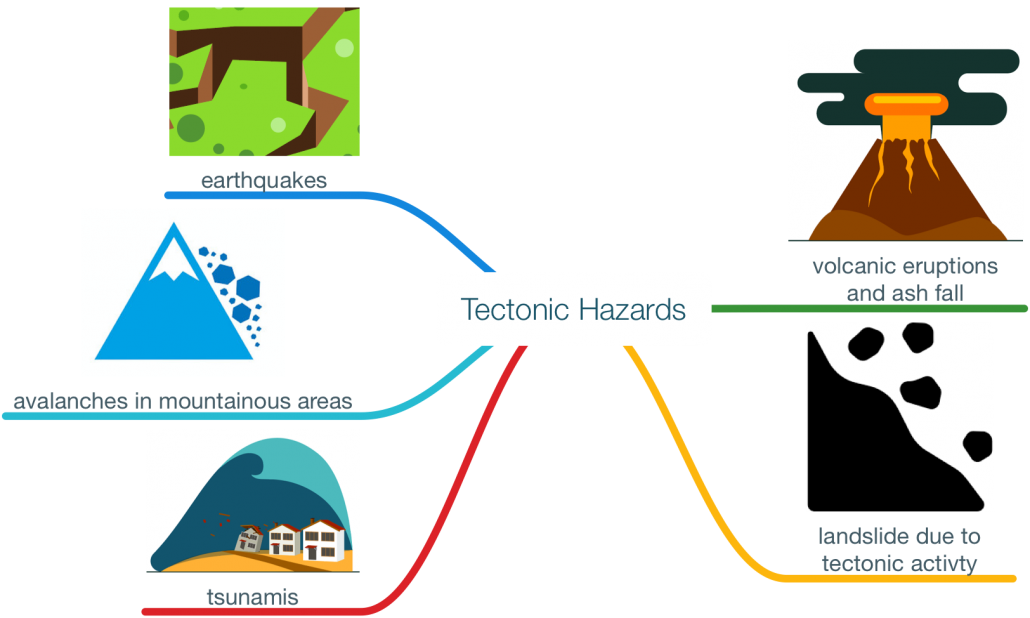
Tectonic hazards
Hazards to humans created in the atmosphere, such as tropical storms, droughts and tornadoes, are atmospheric hazards.
Hazards originating on or near the Earth’s surface, such as landslides, flooding and mudflows, are considered geomorphological hazards.
Hazards posed by living things, e.g. forest fires, are biological hazards.
Factors Affecting Hazard Risk
Natural events, such as volcanic eruptions or earthquakes that occur away from humans and properties, are not considered natural hazards. They are considered natural hazards when they happen close to human populations and property.
Hazard risk is the probability or chance that a natural hazard may take place.
Different factors affect the hazard risk from natural hazards. These are:
- Urbanisation – densely populated areas are at greater risk of natural hazards;
- Development – higher-income countries (HICs) are better equipped to cope with natural hazards than lower-income countries (LICs). This is because they have better infrastructure, emergency response and systems for monitoring and predicting natural hazards. They also have better health care systems and more money to protect people, e.g. earthquake-proof buildings;
- Land use – Changes in land use, e.g. deforestation and urbanisation, can increase hazard risk for climatic and geomorphological hazards;
- Climate change – The magnitude and frequency of some climatic hazards, including droughts and tropical storms, will be affected by climate change.
- Geographical location – some places are more at risk of natural hazards because of where they are. For example, countries around the Pacific Ring of Fire are more at risk of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes than those elsewhere. Additionally, as temperatures get warmer due to climate change, more tropical storms will affect countries in the tropics.
Summary
Flashcards
Quiz
What is a natural hazard?
Natural events, such as volcanic eruptions or earthquakes that occur away from humans and properties are not considered natural hazards.
Which of the following factors affect the risk from natural events such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and floods?
All of these factors affect risk from natural events.
What is a tectonic hazard?
Which of the following is an example of a tectonic hazard?
What is a climatic hazard?
Which hazard is caused by rising temperature?
What type of hazard is a tsunami?
Which of the following is not a factor that affects hazard risk?
True or false? An increase in the frequency and magnitude of a natural hazard can affect hazard risk.



Share your Results:
