What are the causes of drought?
A drought is a severe shortage of water in a particular location. A combination of factors causes droughts.
Meteorological causes of drought
Meteorological factors can cause an area to get less rainfall than average. Changes in global atmospheric circulation can mean it doesn’t rain much in an area. For example, the drought in Australia in the 2000s was made worse by changing air and ocean currents in the Pacific Ocean.
Changes in atmospheric circulation can also affect rainfall patterns. In the past, monsoon rains in India had failed to appear when they were due.
High-pressure systems can block low-pressure systems that bring rainfall to the UK. This can lead to drought conditions.
Hydrological causes of drought
A lack of water in stores such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs and aquifers (water stored underground naturally) can lead to drought. Areas that rely on rainfall and surface water are more likely to experience drought. Surface water quickly evaporates in warm, dry conditions leading to an increased risk of drought.
Hydrological causes of drought can take some time to have an impact. For example, water stores such as aquifers can take months or even years to replenish.
Human causes of drought
Deforestation leads to less water being stored in the soil. Therefore, the land dries out quicker than it would if it were covered in vegetation. Also, trees release moisture into the atmosphere through their leaves, a process is known as transpiration. Removing trees and vegetation reduces the amount of moisture in the atmosphere making the area drier.
Constructing dams and reservoirs reduces the flow of water downstream. This can lead to drought in other areas. There are several locations worldwide where this could lead to conflict in the future, including along the River Nile.
Intensive agriculture depletes water supplies as large quantities of water are required for irrigation. Additionally, livestock also has considerable demands on water for drinking.
Some locations are more vulnerable to drought than others
The map below shows the distribution of droughts around the world.
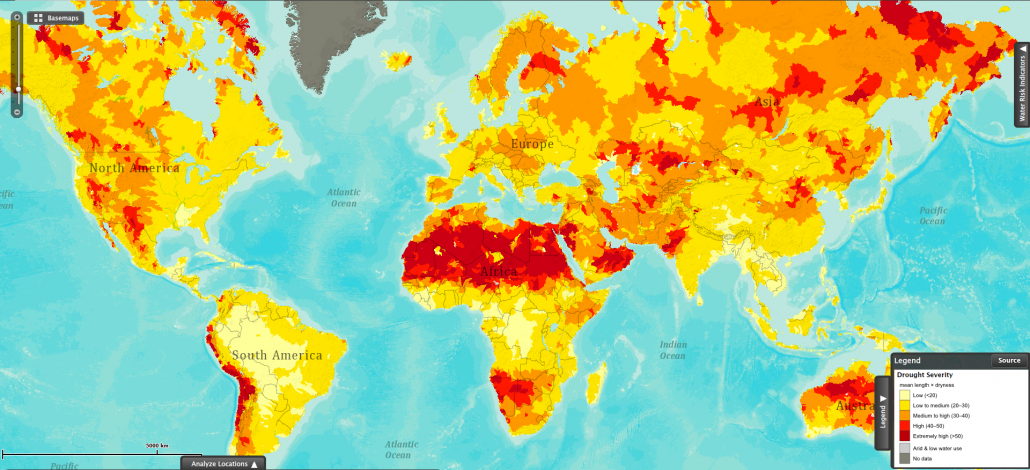
This map shows drought severity, measured as the product of the average length of a drought occurrence and how dry it was the drought. This visualization is based on data collected for the period between 1901 and 2008.
The areas experiencing the most severe droughts occur at around 30° north and south of the equator. This can be explained by global atmospheric circulation, as high pressure at this latitude brings very little rainfall.
Over time the locations affected by drought have varied. For example, there have been more droughts in Africa, Asia and the Mediterranean since 1950 and fewer in the Americas and Russia.
Some scientists have suggested that climate change might increase the frequency and severity of droughts in the future.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.



