What is Acid Rain?
Acid rain refers to any form of precipitation, such as rain, snow, sleet, fog, or dew, that contains higher-than-normal levels of acidic compounds like nitric acid and sulfuric acid. It is a significant environmental issue because of its harmful effects on plants, animals, water bodies, and even man-made structures. Acid rain can occur as either wet deposition (precipitation like rain, snow, fog, etc.) or dry deposition (acidic particles and gases that settle on surfaces without precipitation).
Acid rain is primarily caused by the release of pollutants into the atmosphere from human activities. The two key pollutants responsible for acid rain are sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), both of which are emitted by burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. These pollutants come from several sources:
Once in the atmosphere, these gases react with water vapour, oxygen, and other chemicals to form sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and nitric acid (HNO₃). These acidic compounds mix with cloud water, eventually falling to the Earth as acid rain during precipitation.
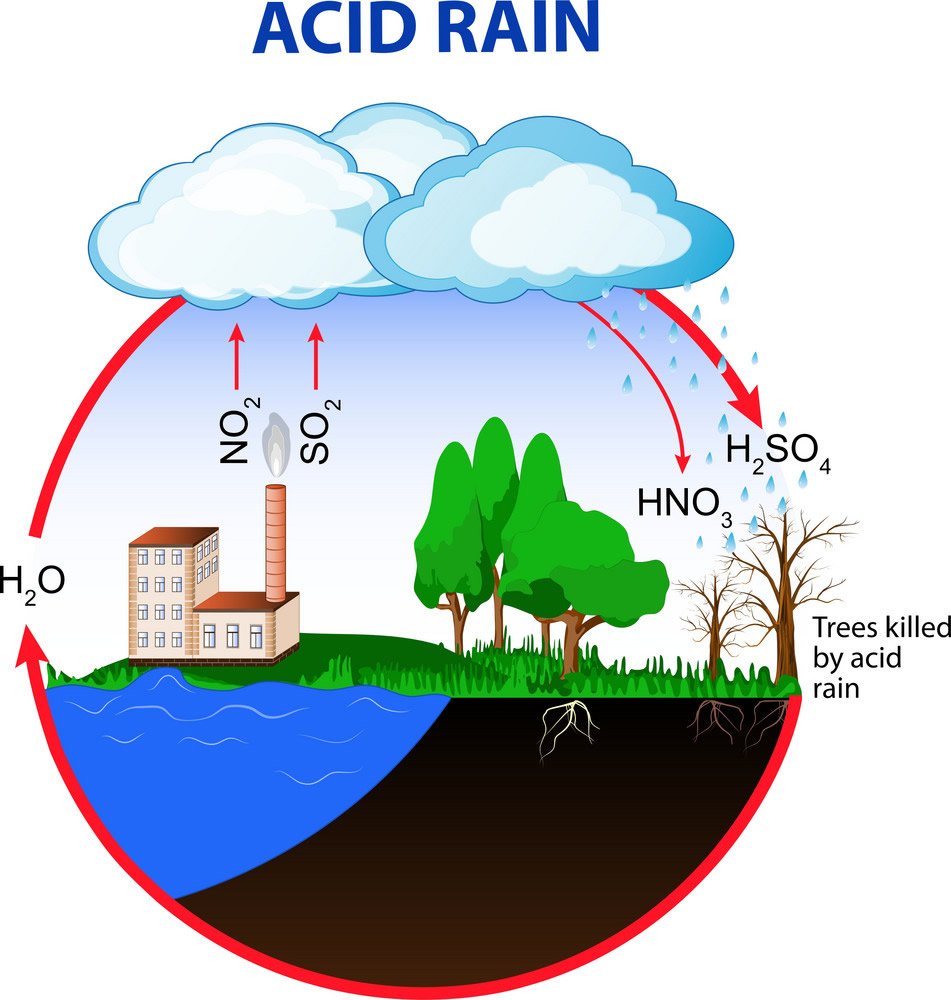
The cause of acid rain
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.