What is convectional rainfall?
Convectional rainfall occurs when the sun’s energy heats the surface of the Earth, causing water to evaporate to form water vapour. When the land heats up, it warms the air above it, causing it to expand and rise. As the air rises, it cools and condenses. This process of condensation forms clouds high in the atmosphere. If this process continues, rainfall will occur. This type of rainfall is widespread in tropical areas (between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn) and in areas such as South East England during warm sunny spells.
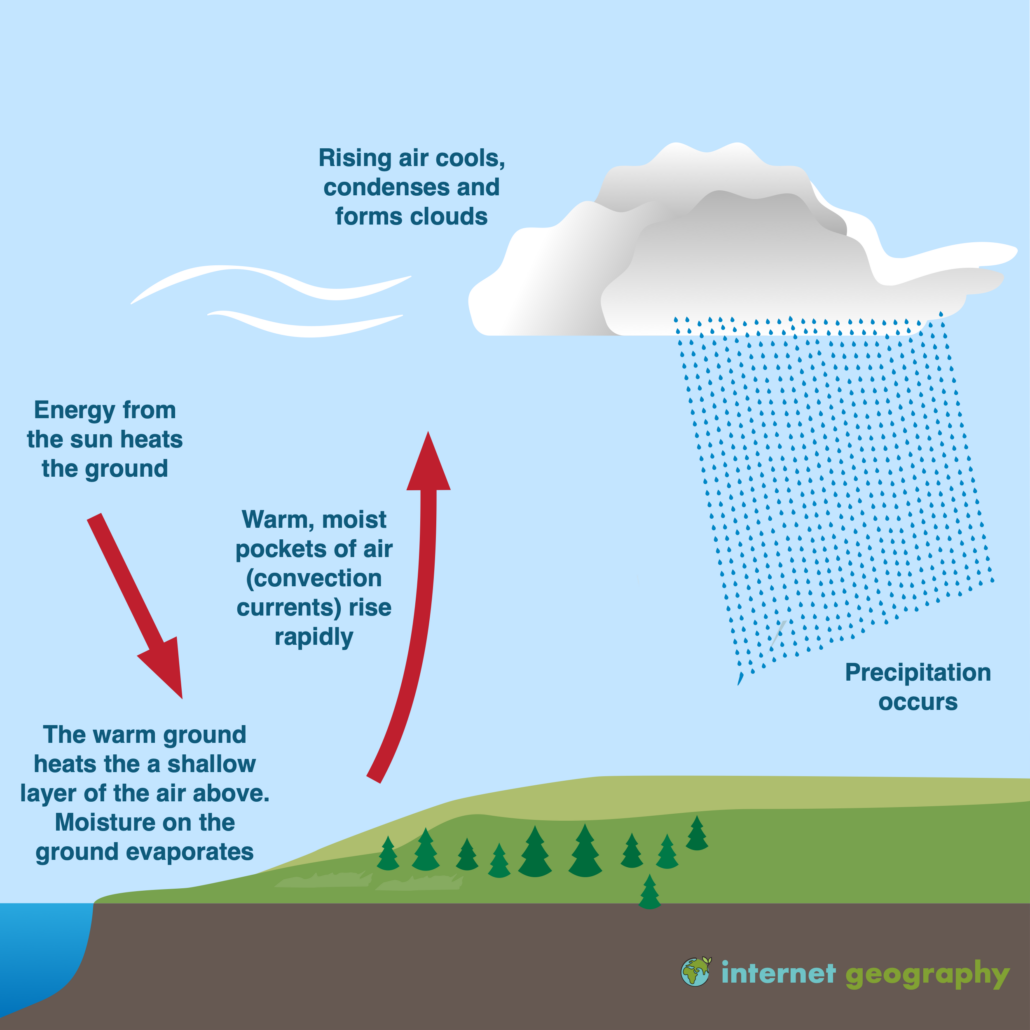
Convectional rainfall
Stage 1.
The sun heats the ground, and warm air rises.
Stage 2
As the air rises, it cools, and water vapour condenses to form clouds.
Stage 3.
When the condensation point is reached, large cumulonimbus clouds are formed.
Stage 4.
Heavy rainstorms occur. These usually include thunder and lightning due to the electrical charge created by unstable conditions.
Convectional rainfall is widespread in areas where the ground is heated by the hot sun, such as the Tropics. This is why areas, such as the Amazon Rainforest, experience heavy rainfall most afternoons.
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.