The Location and Importance of a City in the UK
What is the location and importance of Bristol?
Location:
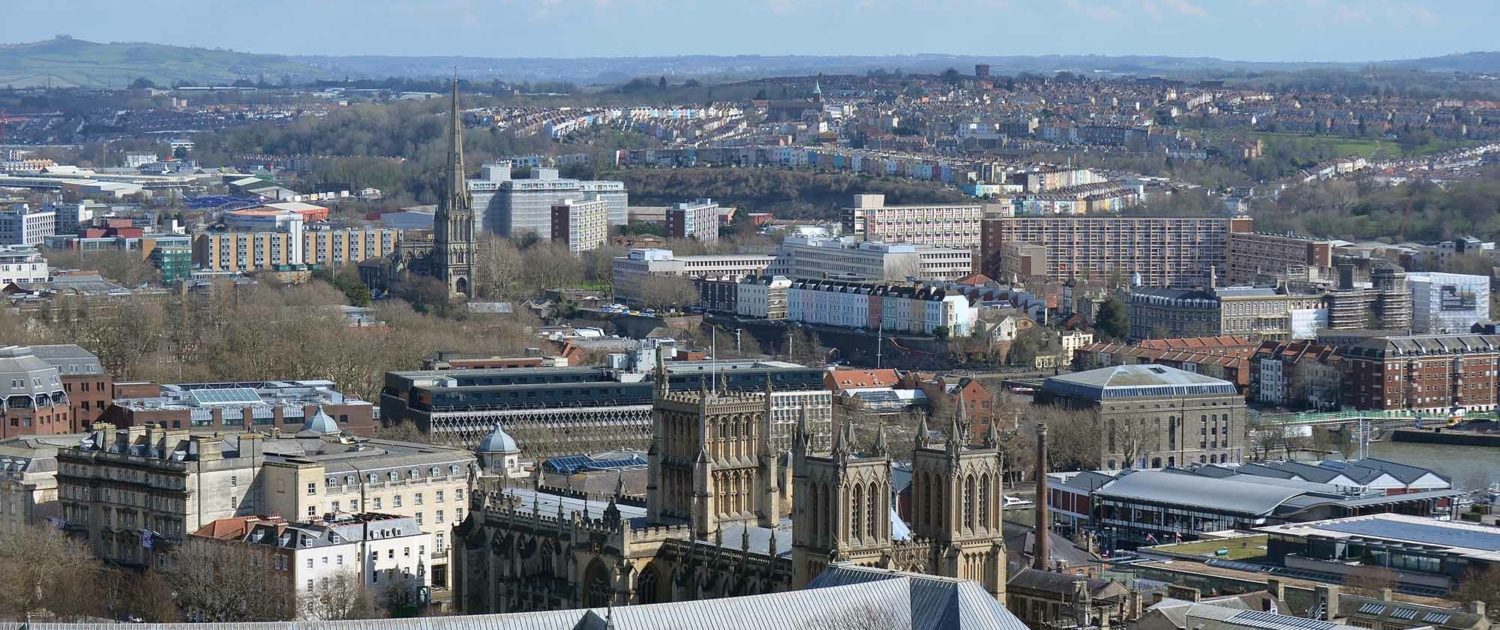
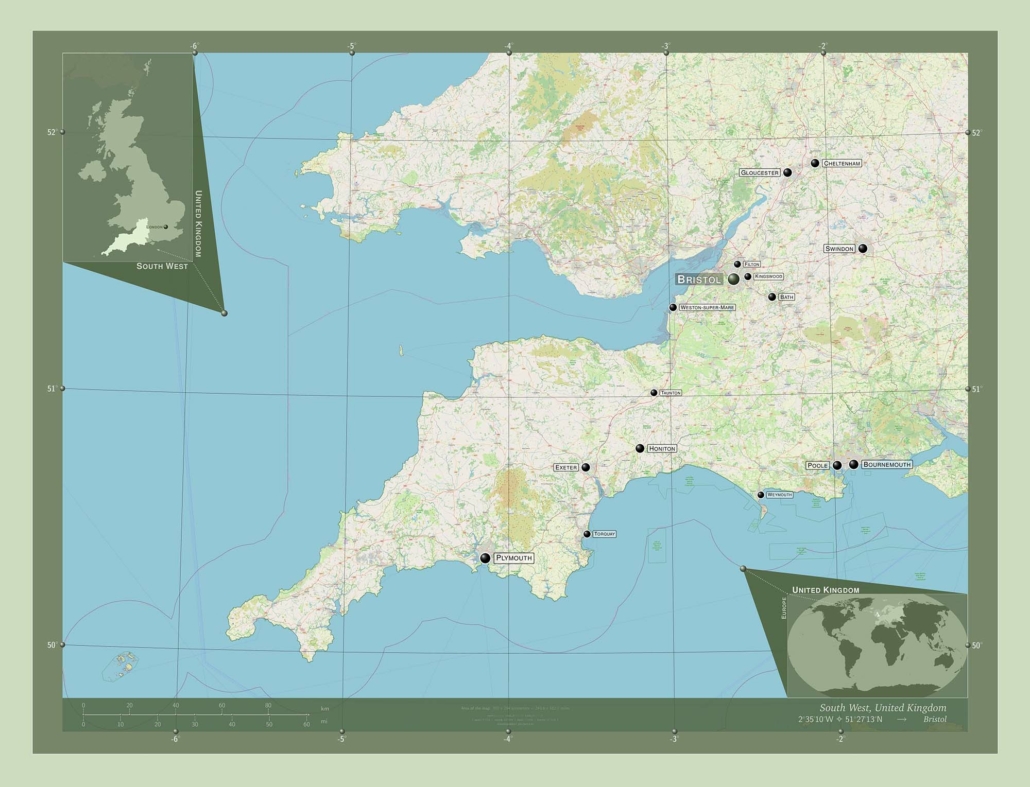
Bristol is located in the southwest of England. It lies approximately 120 miles west of London, at the confluence of the Rivers Frome and Avon. Bristol is near the historic cities of Bath to the southeast and Gloucester to the northeast.
Between the last two censuses (held in 2011 and 2021), the population of Bristol increased by 10.3%, from just over 428,200 in 2011 to around 472,500 in 2021.
The population here increased by a larger percentage than the overall population of the South West (7.8%) and by a greater percentage than the overall population of England (up 6.6% since the 2011 Census).
Bristol developed as a port in the middle ages and supported trade with other countries.
During the 18th century, Bristol expanded due to its integral role in the triangular trade route connecting West Africa and the West Indies. The slave trade thus represents a crucial chapter in Bristol’s past, as the generated wealth significantly fueled the city’s growth. The city is striving to acknowledge this history as it evolves its identity. An illustration of this is the renaming of Colston Hall, originally named after a slave trader, to Bristol Beacon to dissociate from its past.
Bristol is one of the UK’s eleven ‘core cities’ and is a city of regional and national importance.
Importance in the UK:
- Economic Importance: Bristol has a strong economy, with a particular emphasis on the aerospace industry, defence, media, information technology and financial services sectors. Major companies such as Airbus, Rolls-Royce and the BBC have significant bases in Bristol. The city has a high level of inward investment, including Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in manufacturing, finance and hi-tech business.
- Educational Importance: Bristol is home to two major universities: the University of Bristol and the University of the West of England, contributing to a vibrant student population and cutting-edge research facilities.
- Cultural Importance: The city is known for its thriving arts scene, with a rich history in music, film, and theatre. It’s also the birthplace of the internationally renowned street artist Banksy.
- Historical Importance: Bristol played a significant role in England’s maritime history. During the height of the British Empire, it was a major port for trade and a departure point for exploratory voyages.
- Transport Importance: Bristol has excellent transportation links, with a major seaport, an international airport, and good rail and road connections to other parts of the UK.
Importance in the Wider World:
- Economic Importance: Bristol’s economy plays a role in the global marketplace, particularly in the aerospace industry. For example, Airbus in Bristol designs and manufactures wings for all Airbus commercial aircraft. Bristol has the largest concentration of silicon chip manufacture outside California. Today, there are two major docks, located at Avonmouth and Royal Podbury, and is the UK’s most centrally located deep-sea container port. 550000 cars are imported each year from Japan, Korea and Germany. It is the UK’s 8th most popular city for foreign visitors. The University of Bristol has more than 6,750 international students from more than 150 countries.
- Cultural Importance: Bristol’s cultural exports, including its music scene, Banksy’s street art, and Wallace and Gromit animations, have gained international recognition.
- Environmental Importance: Bristol was awarded the European Green Capital Award in 2015, becoming the first UK city to win this prestigious environmental award. This has placed Bristol on the global map as a leading city in terms of environmental sustainability.
- Historical Importance: Bristol’s history as a major player in the transatlantic slave trade links it to many parts of the globe, especially the Caribbean and Africa. This shared history has influenced its diverse population and cultural heritage.
Bristol’s location and importance in the UK and the wider world are marked by its robust economic sectors, historical and cultural significance, environmental sustainability contributions, and role in global trade and education.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.