What is the role of transnational companies in Nigeria?
What is the role of transnational companies in Nigeria’s oil business?
The Niger Delta region, an important wetland and coastal ecosystem, is home to Nigeria’s oil and gas industry. Nigeria’s oil boom took off during the 1970s. It relied on the expertise of large transnational corporations, including:
- Total (France)
- Exxon-Mobil (USA)
- Royal Dutch Shell (UK & Netherlands)
- Chevron (USA)
- Agip (Italy)
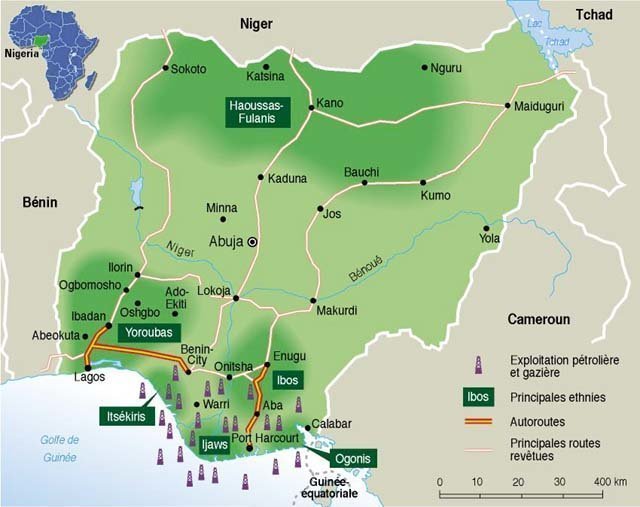
Map of Nigeria with principal ethnic groups and oil & gas resources. Credit: Le Monde, Paris
These multinational companies constructed oil and gas drilling platforms around the Niger Delta. Linked to these platforms, pipelines around the Gulf of Guinea transport oil to large tankers that ship it to Europe and the USA, where it is refined to produce petrol and other oil-based products. Transnational companies make far higher profits from refined oil.
To keep more oil profits within the country, the Nigerian government has set up the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) to form joint ventures with TNCs.
What is the environmental impact of oil in Nigeria?
The Niger Delta region has experienced a range of environmental damage caused by the oil industry. Farmland has been damaged by leaking oil pipes, meaning crops no longer grow in some areas.
Oil pollution from tankers and damaged pipelines kills fish in the sea and the delta. When gas is burned off from the oil, greenhouse gases are released, contributing to climate change. The process also causes respiratory problems for local people.
According to the Guardian, 40 million litres of oil are spilt in the Niger Delta each year compared to 4m in the US.
In the Niger Delta, the contamination of fish and crops has destroyed livelihoods, destroyed local employment opportunities and pushed many into militancy. Life expectancy in the Niger Delta is ten years below the national average.
The government has established laws to protect the environment from oil exploration. However, for these to be effective, responsible agencies must implement, enforce, and monitor them effectively.
Below is a video exploring the impact of exploiting fossil fuels in the Niger Delta.
De-ruralization of the Niger Delta: Reconsidering Rurality in the Urbanization Discourse from Sourav Kumar Biswas on Vimeo.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of TNCs?
Advantages of TNCs include:
- international links that provide access to markets around the world
- bringing financial investment into the host country’s economy
- providing jobs and training to local people
- higher wage levels
- introducing new technology that might otherwise not be available
Disadvantages of TNCs include:
- profits leave the country and benefit shareholders, often in HICs
- paid wages tend to be lower than in the home country of the TNC
- causing significant environmental damage without taking responsibility for cleaning up
- being able to withdraw from a country if circumstances change
- powerful TNCs can exert pressure on governments
- raw materials are exported before being refined, which reduces profits in LICs and NEEs
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.



