Western Desert Case Study
What are the opportunities and challenges to economic development in the Western Desert (USA)?
The Western Desert extends over 200,000 square kilometres and is located in the southwest of the USA. The Western Desert comprises three deserts: the Sonoran Desert, the Mojave Desert and the Chihuahuan Desert. It extends across several states, including California, New Mexico and Arizona.
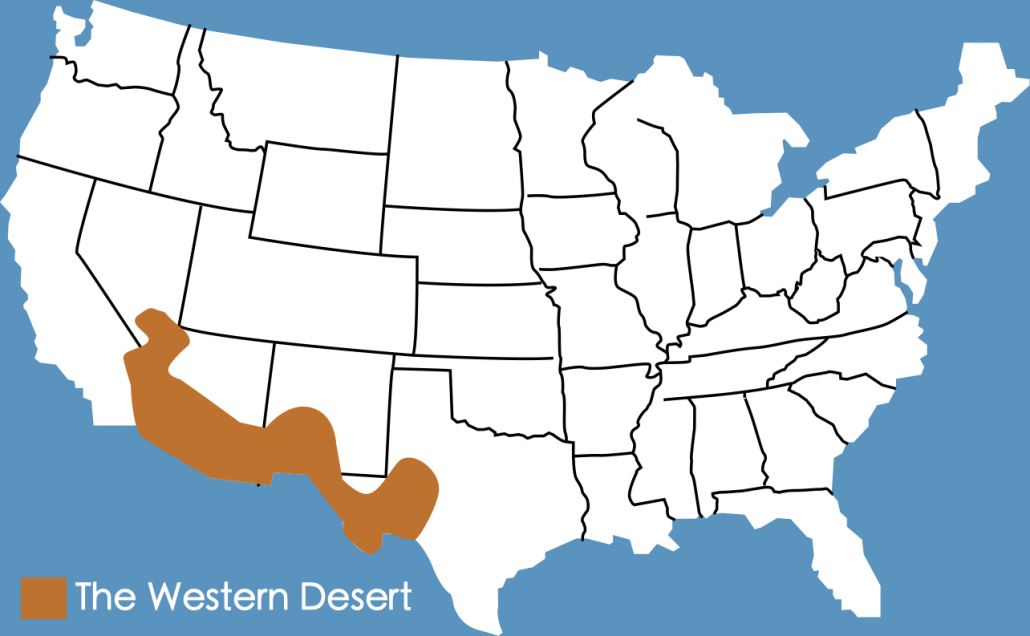
A map to show the location of the Western Desert
The Western Desert has a low population density with the majority of its inhabitants living in large cities such as Las Vegas and Phoenix, Arizona.
Mineral extraction in the Western Desert
Many minerals are extracted from the ground in the Western Desert, including:
Energy in the Western Desert
A range of renewable and non-renewable energy resources are exploited in the Western Desert. Renewable energy resources include solar energy and hydroelectric power (HEP). In the Sonoran Desert, enough solar energy is produced to power 100,000 homes. Due to the long hours of sunshine, there is massive potential for solar energy generation. A dam has been constructed on Lake Mead to generate HEP.
In Arizona, there are large reserves of oil being extracted from the land.
Farming in the Western Desert
Most farming in the Western Desert is commercial, meaning farms grow produce to sell. In the Coachella Valley, water is extracted from aquifers to grow crops such as peppers and grapes. Irrigation water from Lake Mead is used in farming.
Tourism in the Western Desert
Tourism is a significant industry in the Western Desert. Many tourists visit natural attractions such as the Grand Canyon alone. Lake Mead is a popular location for water sports. Las Vegas attracts over 31 million visitors every year.

Las Vegas
Hot deserts are hostile, remote and challenging environments for development.
Water supply in the Western Desert
Precipitation levels in the Western Desert are very low at around 55mm per year, and evaporation rates are high. Stable water supplies are essential for economic development. To meet demand, the Hoover Dam was constructed on the Colorado River to provide water for drinking and irrigation.
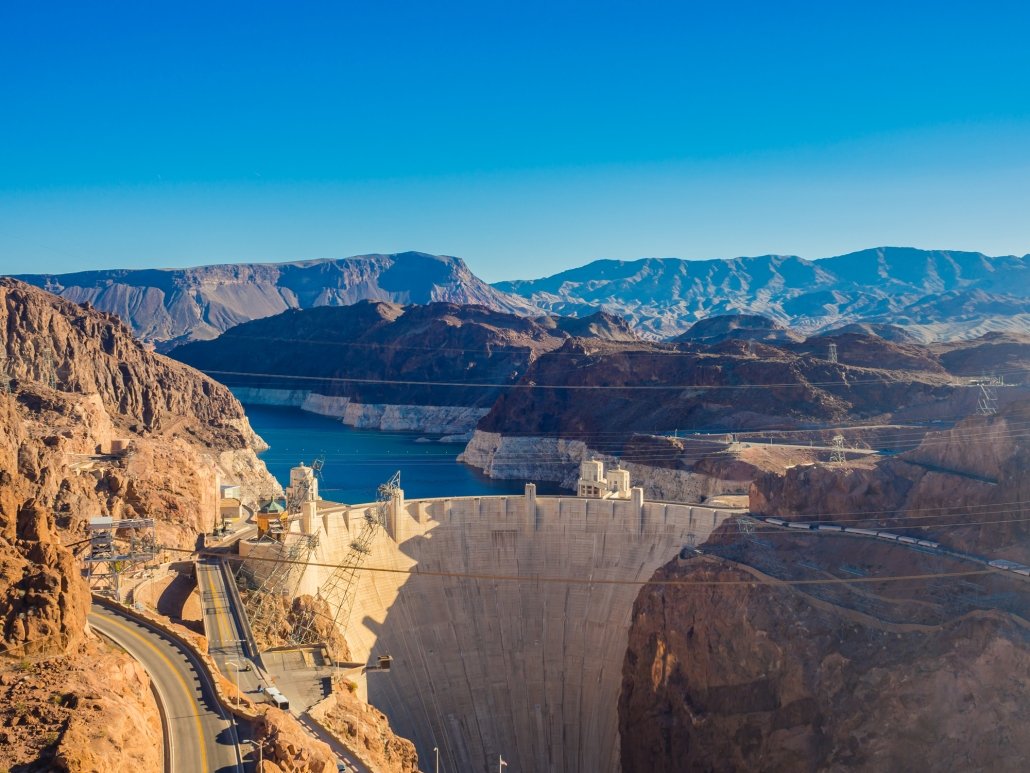

The Hoover Dam on the Colorado River.
Population growth in major cities such as Phoenix increases pressure for water.
Inaccessibility and the Western Desert
Access in the Western Desert is limited to major cities such as Chicago and Las Vegas. Major routes such as Route 66 provide links to major urban areas.

Mohave Desert by Route 66 in California, USA
A large proportion of roads are unsurfaced.
Extreme Temperatures in the Western Desert
Temperatures can exceed 49°C in the Western Desert, which makes it very challenging for people, such as farmers, to work outside. High temperatures lead to rapid evaporation and a shortage of water.
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.